Protein is an indispensable component for various bodily functions, weight management, and muscle development.
It’s crucial to acquire adequate protein through diet, with medical experts recommending that at least 10% of daily caloric intake should be derived from protein sources.
Foods like chicken, eggs, pulses, fish, nuts, milk, and yogurt are rich sources of protein. However, understanding the signs of protein deficiency is essential for maintaining overall health.
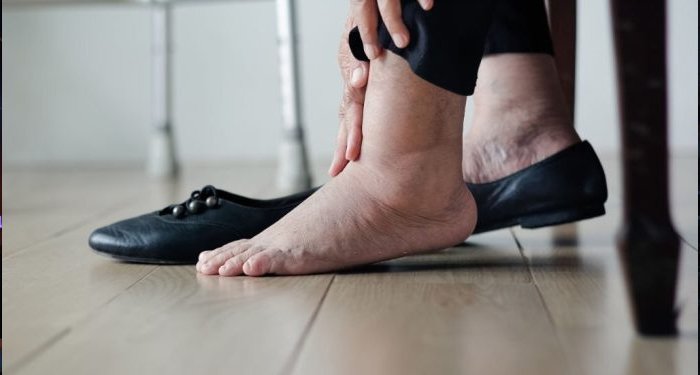
Edema – Swelling of Extremities:
One prevalent symptom of protein deficiency is the swelling of hands, feet, and legs. Proteins play a pivotal role in preventing fluid accumulation in organs during circulation. While several factors can cause edema, protein deficiency can contribute to it. Consulting a medical professional is crucial for an accurate diagnosis.
Mood Disturbances and Irritability:
Proteins are the building blocks of neurotransmitters, chemicals vital for brain communication. Neurotransmitters, like dopamine and serotonin, which influence mood, are derived from amino acids found in proteins. Inadequate protein intake can lead to imbalanced neurotransmitter production, resulting in mood disorders such as irritability and even depression.
Impaired Hair, Nail, and Skin Health:
Proteins like collagen and keratin are pivotal for healthy hair, nails, and skin. Inadequate protein levels can lead to brittle, thin hair, weakened nails, and compromised skin health. Protein deficiency increases the risk of conditions like baldness and overall poor skin appearance.
Muscle Weakness and Fatigue:
Studies indicate that insufficient protein intake can lead to muscle weakness, especially in muscles necessary for movement. Over time, sustained protein deficiency can result in muscle mass reduction, slowing metabolism and potentially causing anemia. Anemia contributes to fatigue and overall weakness.
Increased Appetite:
Protein serves as a satiating nutrient, and research suggests that its scarcity can trigger heightened hunger. Adequate protein consumption helps sustain feelings of fullness, aiding in weight management and appetite control.
Delayed Wound Healing:
Collagen, essential for skin health and wound healing, requires adequate protein levels for production. Protein deficiency can hinder collagen synthesis, leading to slower wound healing. Additionally, proteins play a role in blood clotting, further affecting the body’s ability to recover.
Weakened Immune System:
Amino acids derived from proteins play a critical role in the immune system’s function, aiding in antibody production to combat infections. Protein deficiency weakens the immune response, increasing the susceptibility to frequent illnesses.
It’s important to note that these observations are based on peer-reviewed medical research. Individuals should consult their healthcare professionals before making any dietary or lifestyle changes. By being aware of the signs of protein deficiency, individuals can take proactive steps to ensure their nutritional needs are met for optimal health and well-being.